Last week, a MIT study sent shockwaves through the AI and business community: 95% of AI pilots fail to deliver measurable business returns. Headlines spread fast, with investors and executives questioning whether enterprise AI is a bubble.
But behind the headlines lies a more nuanced story. The study doesn’t show that AI lacks potential—it shows that most organizations are not yet equipped to turn AI experiments into real business impact.
Myth vs. Reality: What Other Research Tells Us
While the MIT report highlights execution gaps, other studies paint a more balanced picture:
- McKinsey (2025): AI adoption is rising fast, with value emerging where firms rewire processes and governance.
- Stanford AI Index (2025): Investment and adoption continue to accelerate, signaling confidence in the long-term upside.
- Field studies: Copilots in customer service and software engineering deliver double-digit productivity gains—but only when properly integrated.
- MIT SMR–BCG: Companies that give individuals tangible benefits from AI—and track the right KPIs—are 6x more likely to see financial impact.
The picture is clear: AI works, but only under the right conditions.
Why AI Projects Fail (The 10 Traps)
1. No learning loop
Many AI pilots are clever demos that never improve once deployed. Without feedback mechanisms and continuous learning, the system remains static—and users quickly revert to old ways of working.
2. Integration gaps
AI may deliver great results in a sandbox, but in production it often fails to connect with core systems like CRM or ERP. Issues with identity management, permissions, and latency kill adoption.
3. Vanity pilots
Executives often prioritize flashy use cases—like marketing campaigns or customer-facing chatbots—while ignoring back-office automations. The result: excitement without measurable cash impact.
4. Build-first reflex
Organizations rush to build their own AI tools, underestimating the complexity of User eXperience (UX), guardrails, data pipelines, and monitoring. Specialist partners often outperform in speed and quality.
5. Six-month ROI traps
Leadership expects visible returns within half a year. But AI adoption follows a J-curve: disruption comes first, with benefits only materializing once processes and people adapt.
6. Weak KPIs
Too many pilots measure activity—such as number of prompts or usage time—rather than outcomes like error reduction, cycle time improvements, or cost savings. Without the right metrics, it’s impossible to prove value.
7. No product owner
AI projects often sit “between” IT, data, and the business, leaving no single accountable leader. Without an empowered product owner with a P&L target, projects stall in pilot mode.
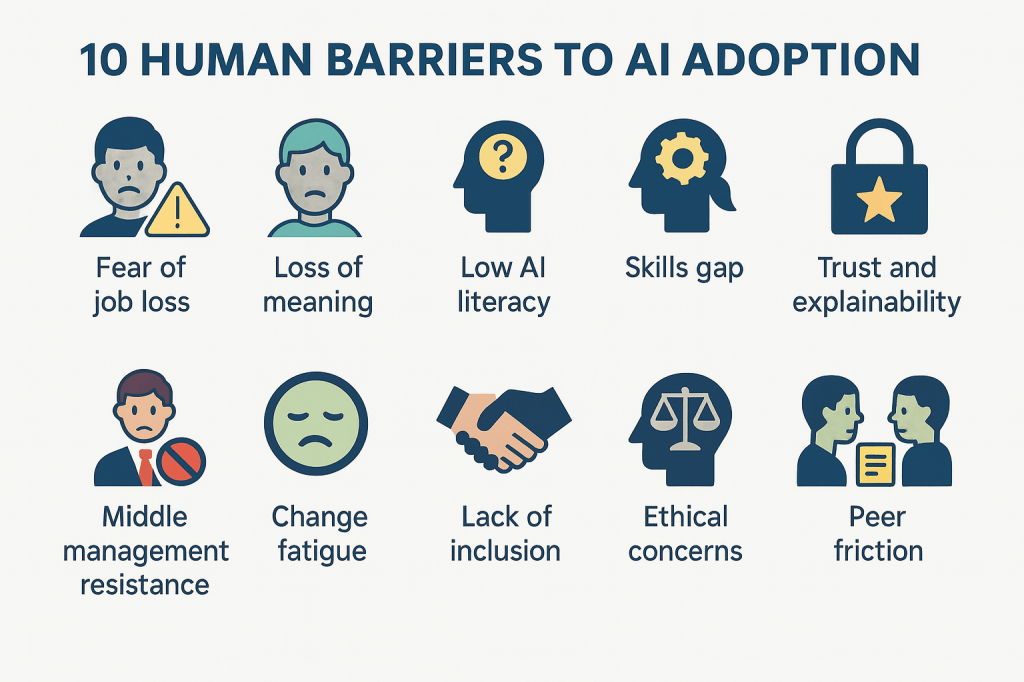
8. Change ignored
Technology is deployed, but users aren’t engaged. Poor UX, lack of training, and trust concerns mean adoption lags. In response, employees turn to consumer AI tools instead of sanctioned ones.
9. Data & policy drag
Even when the AI works, poor data quality, fragmented sources, and unclear governance delay rollouts. Legal and compliance teams often block scaling because policies are not defined early enough.
10. Wrong first bets
Too many companies start with complex tasks. Early success is more likely in “thin-slice” repetitive processes—like call summarization or contract intake—that can prove value quickly.
How to Beat the Odds (10 Fixes That Work)
1. Design for learning
Build AI systems with memory, feedback capture, and regular improvement cycles. If a tool cannot learn and adapt in production, it should never progress beyond pilot stage.
2. Fix integration before inference
Prioritize robust connections into your CRM, ERP, and ticketing systems. AI without seamless workflow integration is just an isolated chatbot with no business impact.
3. Pick quick-win use cases
Target repetitive, document- and conversation-heavy flows—like claims processing, contract extraction, or helpdesk queries. These areas deliver ROI within 90–120 days and build momentum.
4. Appoint an AI Product Owner
Every use case should have a leader with budget, KPIs, and authority. This person is responsible for hitting targets and driving the project through pilot, limited production, and full scale-up.
5. Measure outcomes, not activity
Define 3–5 hard business KPIs (e.g., −25% contract cycle time, −20% cost per contact) and track adoption leading indicators. Publish a regular value scorecard to make progress visible.
6. Buy speed, build advantage
Use specialist vendors for modular, non-differentiating tasks. Save your in-house resources for proprietary applications where AI can become a true competitive edge.
7. Rebalance your portfolio
Shift investments away from glossy front-office showcases. Focus on back-office operations and service processes where AI can cut costs and generate visible ROI quickly.
8. Make change a deliverable
Adoption doesn’t happen automatically. Co-design solutions with frontline users, train them actively, and make fallback paths obvious. Manage trust as carefully as the technology itself.
9. Educate the board on the J-curve
Set realistic expectations that ROI takes more than six months. Pilot fast, but give production deployments time to stabilize, improve, and demonstrate sustained results.
10. Prove, then scale
Choose two or three use cases, set clear ROI targets up front, and scale only after success is proven. This disciplined sequencing builds credibility and prevents overreach.
The Broader Reflection
The 95% failure rate is not a verdict on AI’s future—it’s a warning about execution risk. Today’s picture is simple: adoption and investment are accelerating, productivity impacts are real, but enterprise-scale returns require a more professional approach.
We’ve seen this pattern before. Just as with earlier waves of digital transformation, leaders tend to overestimate short-term results and underestimate mid- to long-term impact.