Innovation has always been a critical driver of competitive advantage, but the demands on innovation today are more intense than ever. Companies need to not only generate breakthrough ideas but also bring them to market rapidly and tailor them to increasingly diverse customer needs.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a transformative force in this landscape. It accelerates every stage of the innovation process—from identifying opportunities and generating concepts to prototyping, testing, and scaling. Just as importantly, AI enables a new level of real-time customisation, empowering businesses to design and refine products and services that are more precisely aligned with individual customer preferences.
In this newsletter, I explore how AI is transforming each phase of the product and service innovation lifecycle, supported by research evidence and real-world applications.
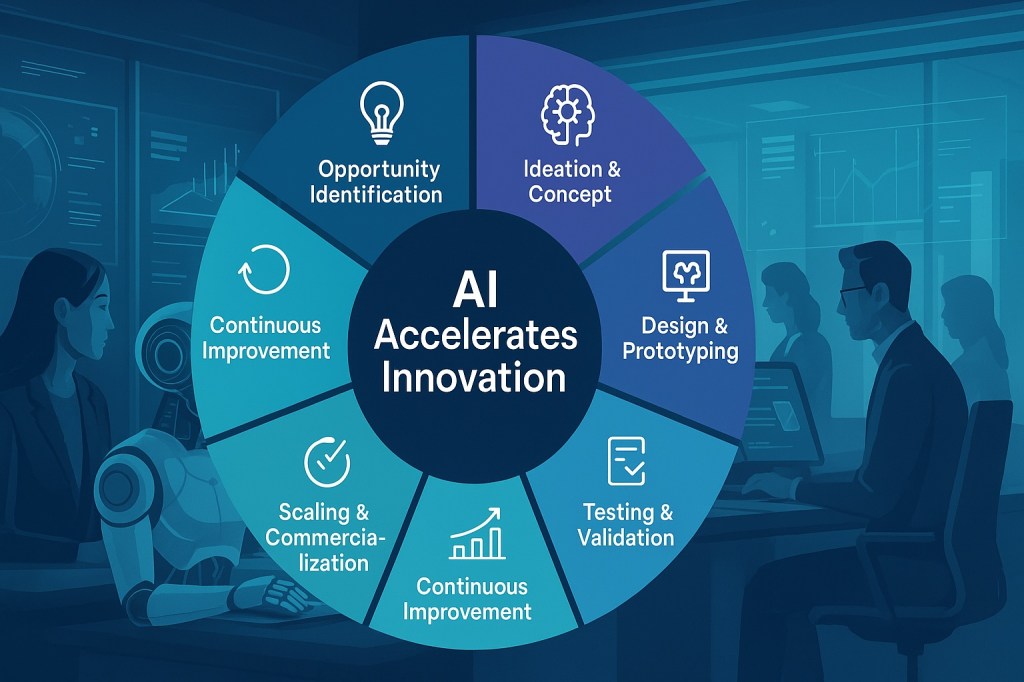
1. Research & Opportunity Identification AI enhances the discovery of new product and service opportunities by analyzing vast volumes of structured and unstructured data—from customer sentiment and social chatter to competitive intelligence and emerging macro trends. Machine learning and natural language processing enable companies to identify unmet needs and whitespace opportunities with speed and precision that traditional market research can’t match.
Research Evidence
- McKinsey (2023): AI accelerates opportunity identification by 37%.
- MIT (2023): Trend analysis with AI improves opportunity detection by 42%.
Examples
- Procter & Gamble uses NLP to mine social media and reviews for unmet customer needs.
- Netflix identifies content gaps via recommendation engine data, informing production.
2. Ideation & Concept Development AI acts as a co-pilot for creativity, expanding the range of ideas and increasing the novelty of concepts generated. Generative AI and collaborative platforms help teams break cognitive biases, synthesize divergent thinking, and visualize concepts early in the process.
Research Evidence
- Stanford Innovation Lab (2022): AI-enhanced brainstorming boosts novel ideas by 56%.
- IBM: Cross-functional ideation quality rises by 31% with AI tools.
Examples
- Airbus generated over 60,000 aircraft partition designs, discovering a solution 45% lighter than legacy models.
- Designers leverage DALL·E to visualize product concepts rapidly.
3. Design & Prototyping AI accelerates prototyping by running simulations, optimizing form factors, and suggesting alternatives based on performance or customer preferences. It reduces development time while improving the diversity and feasibility of design iterations.
Research Evidence
- MIT Media Lab: Iteration time reduced by 47%; 215% more design variations explored.
- Harvard Business Review: AI simulation reduces physical prototype needs by 39%.
Examples
- Volkswagen runs thousands of virtual car tests before building physical versions.
- IKEA uses generative AI for furniture design and visualization.
4. Testing & Validation AI transforms validation by simulating real-world use, forecasting product success, and optimizing features through automated A/B testing. It helps teams reduce risk while aligning products more closely with customer expectations.
Research Evidence
- Forrester (2024): AI improves A/B testing effectiveness by 28%.
- Cambridge University: Product-market fit predictions enhanced by 41% with AI.
Examples
- Amazon simulates user responses to product iterations.
- Unilever uses digital twins to test product performance across different markets.
5. Scaling & Commercialization AI optimizes go-to-market strategies by refining product rollouts, forecasting demand, and personalizing marketing campaigns. It enables faster scaling while controlling costs and maximizing uptake.
Research Evidence
- Accenture: Scale-up time reduced by 31%, costs by 26% through AI.
- MIT Sloan: AI-guided marketing improves product adoption by 23%.
Examples
- Starbucks uses AI to fine-tune new product rollouts globally.
- Toyota leverages AI in supply chain modelling, improving scale efficiency by 18%.
6. Continuous Improvement AI closes the loop in innovation by turning customer usage and feedback into actionable insights. From predictive maintenance to feature enhancement prioritization, AI ensures products remain relevant and valuable over time.
Research Evidence
- Deloitte: AI feedback analysis speeds product improvement cycles by 43%.
- Harvard Business School: Predictive maintenance extends product lifecycles by 27%.
Examples
- Tesla continuously improves vehicles via AI-analyzed driving data with over-the-air updates.
- Microsoft uses AI to prioritize software feature improvements based on user behaviour.
Conclusion AI is more than a technological enabler—it is a strategic accelerator of innovation. By embedding AI across the full product and service lifecycle, companies gain the ability to move faster, personalize smarter, and innovate with greater confidence.
As generative and predictive technologies mature, organizations that embrace AI-driven innovation will shape the future.








