Last week, I had the opportunity to present at the Digital Forum in Amsterdam, where over 100 executives and transformation leaders gathered to explore the future of leadership in the digital era. My keynote, titled “AI Without Borders – Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Global Impact”, was met with great engagement and sparked many thoughtful discussions afterward.
In this article, I’d like to share the highlights and insights from the session—with the slides embedded between paragraphs for context.
AI is Reshaping Work—Across All Roles and Industries
My opening message was simple: no matter where you work or what your role is, AI will impact your processes, job content, and organization over the next 5 to 10 years. The only uncertainty is the scale and speed of this change.
To reinforce this, I brought in research findings from the WEF, MIT, PwC, McKinsey, Gartner, IBM, and Goldman Sachs. These sources highlight both the immense economic potential of AI (up to $15.7 trillion by 2030) and its disruptive impact on the workforce—millions of jobs created, transformed, or displaced, and a pressing need for upskilling on a global scale.

Staying Ahead: Why AI Fluency Matters
One statement particularly resonated with the audience: “It’s not that your job will be replaced by AI—but it might be replaced by someone who uses AI better than you.”
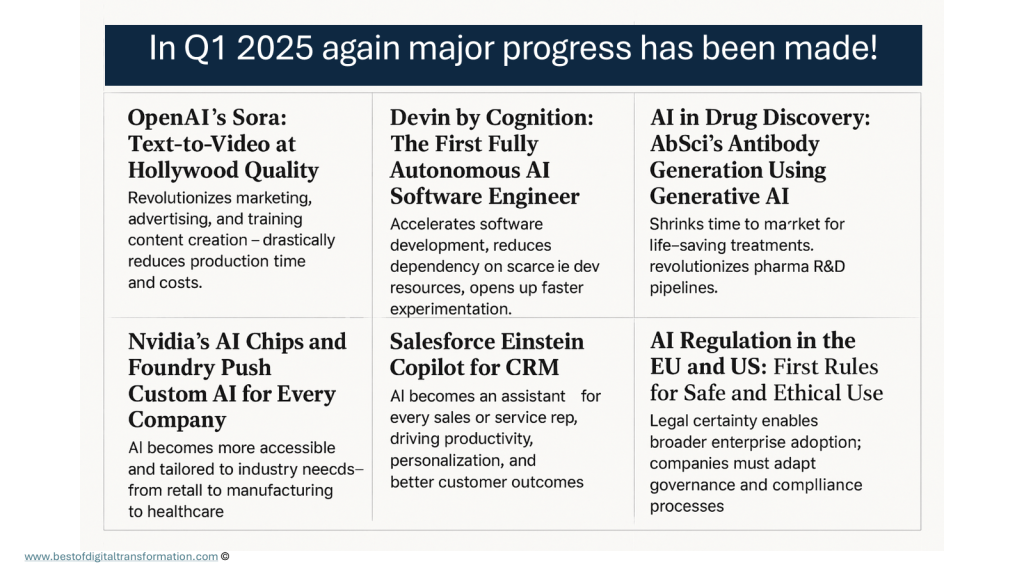
This is a wake-up call for continuous learning. The pace of development is breathtaking. I shared a snapshot of Q1 2025 breakthroughs and hinted at Google’s recent launch of AgentSpace, which I’ll cover in a future edition.
The Real Impact: AI in Marketing, Supply Chain, and Innovation
We then looked deeper into three core business areas—Marketing & Sales, Supply Chain, and Innovation—to see how AI is already creating tangible value.
In Marketing & Sales, AI is now embedded across the funnel—from awareness to retention. At Brenntag, for example, we successfully used AI to predict customer churn and recommend next-best actions, helping our commercial teams serve customers more effectively.

I also highlighted how large brands are already using AI to generate marketing content at scale. But the exciting shift is that these same capabilities are now accessible to smaller companies too—lowering the barriers to entry and leveling the playing field.

In Supply Chain, we see a dual reality: some companies still struggle with visibility and fragmented data, while others are unlocking efficiency gains with advanced AI tools. My message here: building end-to-end supply chain visibility is foundational. Only then can AI deliver its full potential.

As an example, I shared how, more than a decade ago at Philips, we began using IoT and early predictive maintenance for MRI machines. Today, this has evolved into a sophisticated system combining sensors, analytics, and AI—ensuring optimal equipment uptime and smooth patient flow in diagnostic imaging.

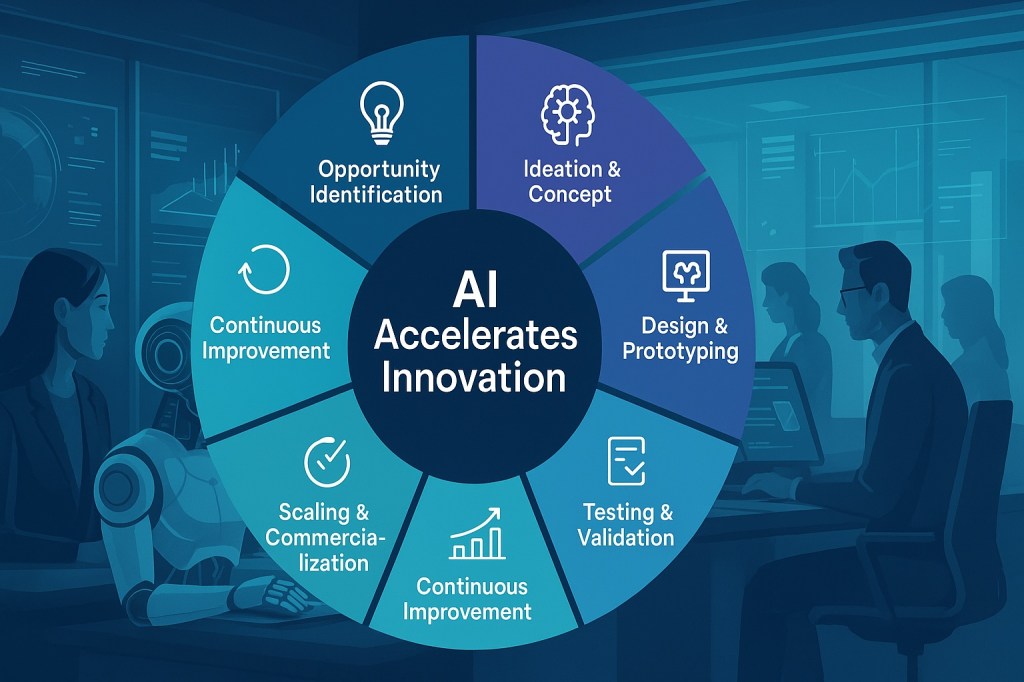
AI Accelerates the Innovation Cycle
AI is also supercharging innovation, reducing the time and cost of development across all phases—from identifying unmet needs to prototyping and testing.

I used the breakthrough example of AlphaFold by DeepMind, which dramatically accelerates drug discovery and the design of new materials. And at Brenntag, we’ve experimented with AI to accelerate lab innovation in the chemical sector—demonstrating that even smaller-scale applications can yield significant gains.

Data: The Essential Fuel for AI
Of course, none of this works without data. But many organizations face persistent challenges: fragmented systems, inconsistent standards, unclear data ownership, and poor governance.
I emphasized that improving data quality, accessibility, and trust is a prerequisite for AI success. Only when teams believe in the data and the systems built on top of it will adoption and results follow.

People and Culture Make the Difference
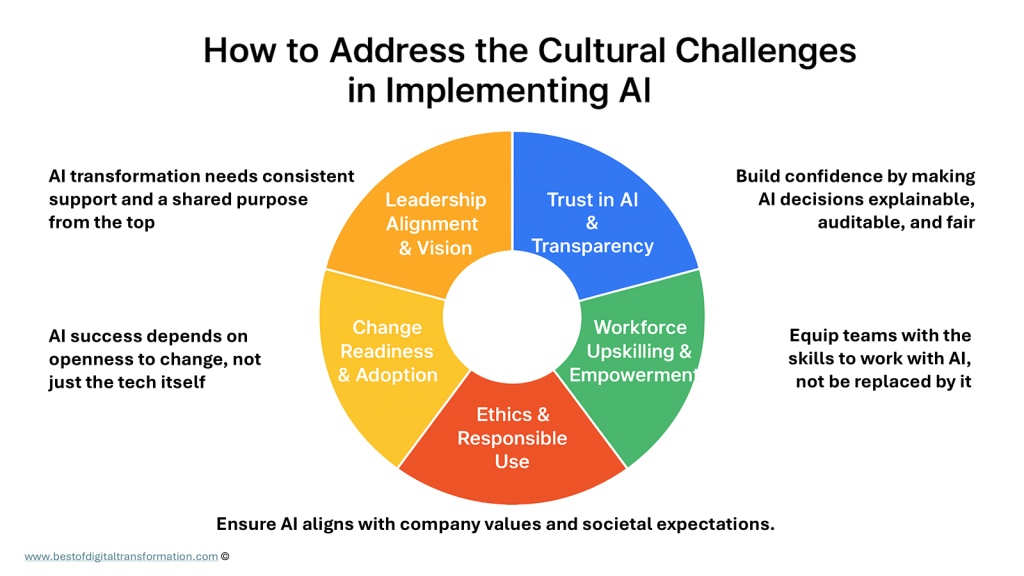
Finally, I addressed the cultural and organizational shifts required for AI to succeed. This includes:
- Building trust and transparency into AI solutions
- Empowering people to work ethically and responsibly with AI
- Driving change management and adoption
- And most importantly: ensuring consistent leadership support, with a clear vision and shared purpose
My Closing Message
I wrapped up with four key takeaways for leaders steering AI transformations:
- AI will change processes, jobs, and businesses – only the speed is unknown
- Data is the fuel for AI – make it fit for purpose and ready to use
- The future is Human + AI – a cultural transformation is essential
- Embed AI in your Operating Model – start small, scale fast, and learn continuously