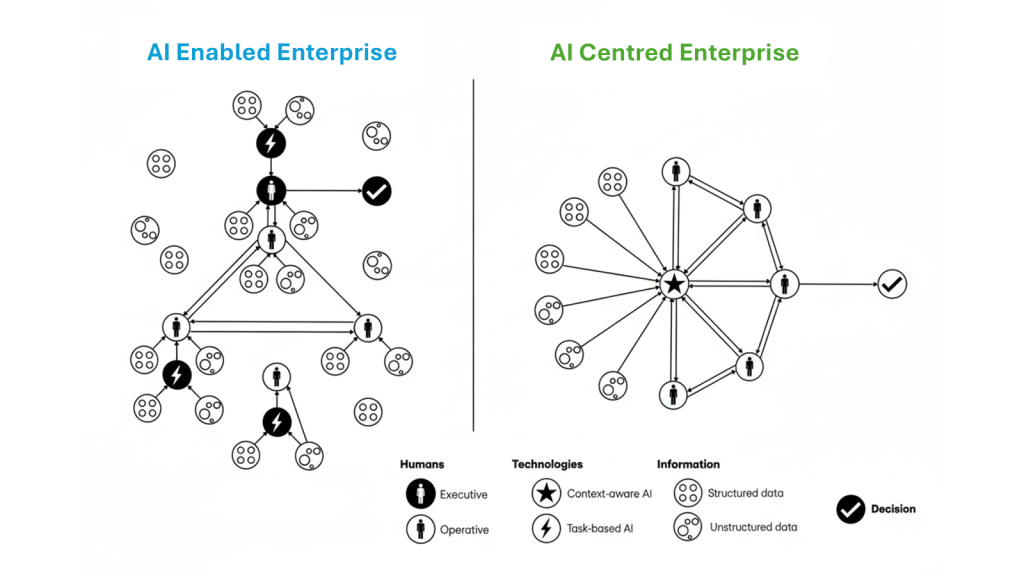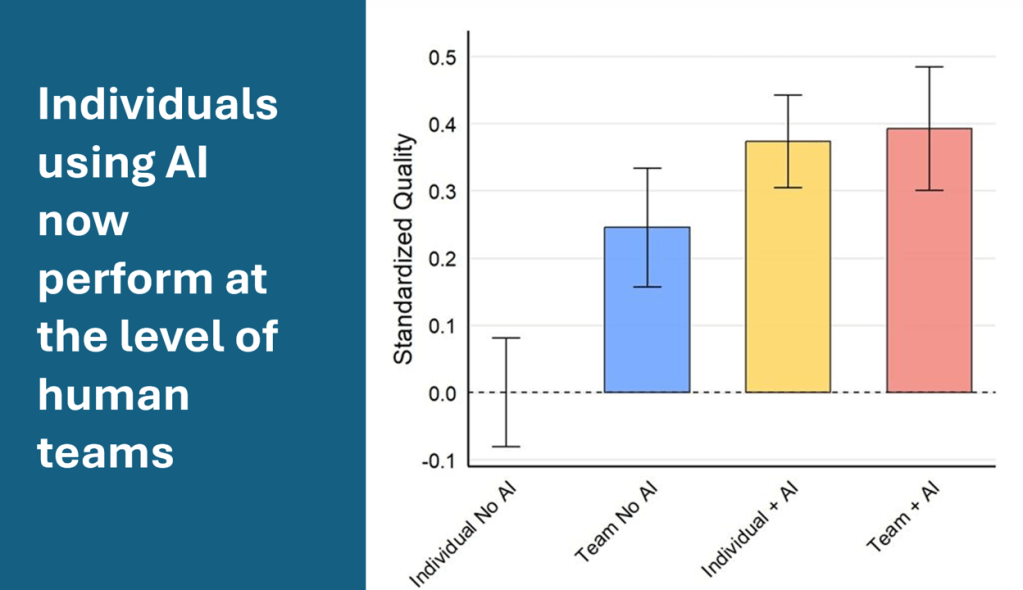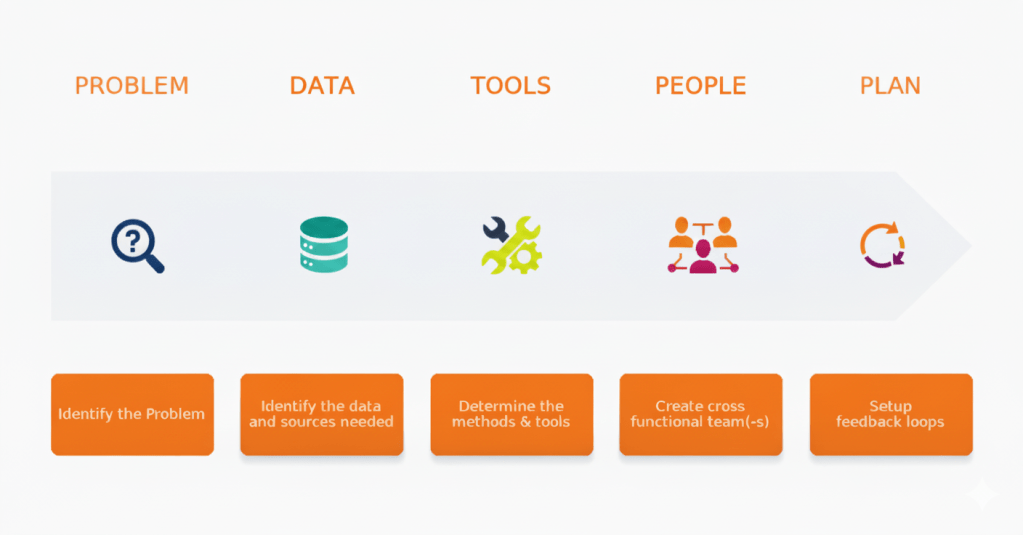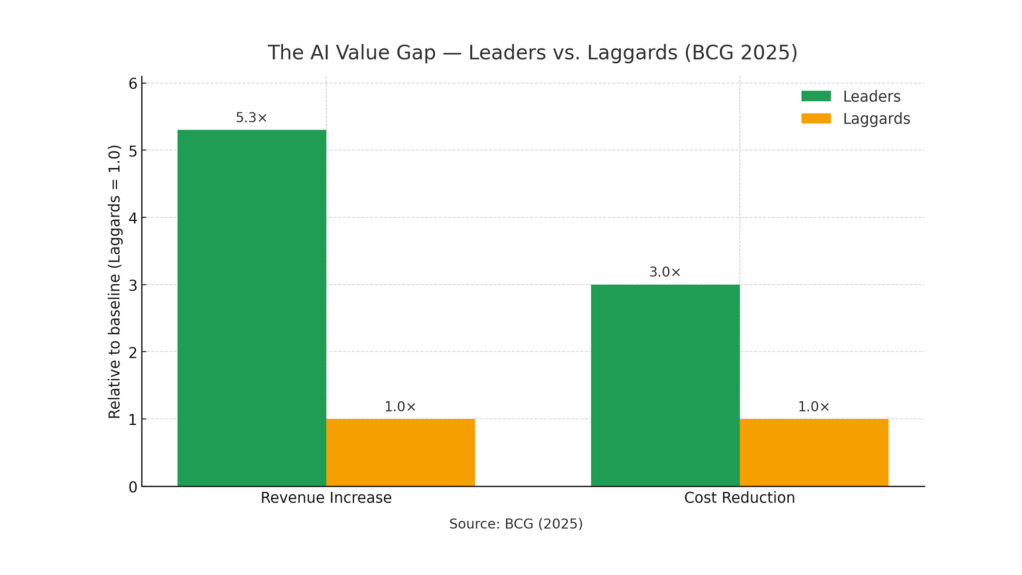
There’s still a value gap—but leaders are breaking away. In the latest BCG work, top performers report around five times more revenue uplift and three times deeper cost reduction from AI than peers. The common thread: they don’t bolt AI onto old processes—they rewire the work. As BCG frames it, the 10-20-70 rule applies: roughly 10% technology, 20% data and models, and 70% process and organizational change. That’s where most of the value is released.
This article is for leaders deciding where to place AI bets in 2025. If you’re past “should we do AI?” and into “where do we make real money?”, this is your map.
Where the money is (cross-industry)
1) Service operations: cost and speed
AI handles simple, repeatable requests end-to-end and coaches human agents on the rest. The effect: shorter response times, fewer repeat contacts, and more consistent outcomes—without sacrificing customer experience.
2) Supply chain: forecast → plan → move
The gains show up in fewer stockouts, tighter inventories, and faster cycle times. Think demand forecasting, production planning, and dynamic routing that reacts to real-world conditions.
3) Software and engineering: throughput
Developer copilots and automated testing increase release velocity and reduce rework. You ship improvements more often, with fewer defects, and free scarce engineering time for higher-value problems.
4) HR and talent: faster funnels and better onboarding/learning
Screening, scheduling, and candidate communication are compressed from days to hours. Internal assistants support learning and workforce planning. The results: shorter time-to-hire and better conversion through each stage.
5) Marketing and sales: growing revenue
Personalization, next-best-action, and on-the-fly content creation consistently drive incremental sales. This is the most frequently reported area for measurable revenue lift.
Leadership advice: Pick 2-3 high-volume processes (one cost, one revenue). Redesign the workflow, not just add AI on top. Set hard metrics (cost per contact, cycle time, revenue per visit) and a 90-day checkpoint. Industrialize what works; kill what doesn’t.
Sector spotlights
Consumer industries (Retail & Consumer Packaged Goods)
Marketing and sales.
- Personalized recommendations increase conversion and basket size; retail media programs are showing verified incremental sales.
- AI-generated marketing content reduces production costs and speeds creative iteration across markets and channels. Mondelez reported 30-50% reduction in marketing content production costs using generative AI at scale.
- Campaign analytics that used to take days are produced automatically, so teams run more “good bets” each quarter.
Supply chain.
- Demand forecasting sharpens purchasing and reduces waste.
- Production planning cuts changeovers and work-in-progress.
- Route optimization lowers distance traveled and fuel, improving on-time delivery.
Customer service.
- AI agents now resolve a growing share of contacts end-to-end. Ikea AI agents now handle already 47% of all request so service people can offer more support on the other questions.
- Agent assist gives human colleagues instant context and suggested next steps.
The result is more issues solved on first contact, shorter wait times, and maintained satisfaction, provided clear hand-offs to humans exist for complex cases.
What to copy: Start with one flagship process in each of the three areas above; set a 90-day target; only then roll it across brands and markets with a standard playbook.
Manufacturing (non-pharma)
Predictive maintenance.
When tied into scheduling and spare-parts planning, predictive maintenance reduces unexpected stoppages and maintenance costs—foundational for higher overall equipment effectiveness (spelled out intentionally).
Computer-vision quality control.
In-line visual inspection detects defects early, cutting scrap, rework, and warranty exposure. Value compounds as models learn across lines and plants.
Production scheduling.
AI continuously rebalances schedules for constraints, changeovers, and demand shifts—more throughput with fewer bottlenecks. Automotive and electronics manufacturers report 5-15% throughput gains when AI-driven scheduling handles real-time constraints.
Move to scale: Standardize data capture on the line, run one “AI plant playbook” to convergence, then replicate. Treat models as line assets with clear ownership, service levels, and a retraining cadence.
Pharmaceuticals
R&D knowledge work.
AI accelerates three high-friction areas: (1) large evidence reviews, (2) drafting protocols and clinical study reports, and (3) assembling regulatory summaries. You remove weeks from critical paths and redirect scientists to higher-value analysis.
Manufacturing and quality.
Assistants streamline batch record reviews, deviation write-ups, and quality reports. You shorten release cycles and reduce delays. Govern carefully under Good Manufacturing Practice, with humans approving final outputs.
Practical tip: Stand up an “AI for documents” capability (standardized templates, automated redaction, citation checking, audit trails) before you touch lab workflows. It pays back quickly, proves your governance model, and reduces compliance risk when you expand to higher-stakes processes.
Healthcare providers
Augment the professional; automate the routine. Radiology, pathology, and frontline clinicians benefit from AI that drafts first-pass reports, triages cases, and pre-populates documentation. Northwestern Medicine studies show approximately 15.5% average productivity gains (up to 40% in specific workflows) in radiology report completion without accuracy loss. Well-designed oversight maintains quality while reducing burnout.
Non-negotiable guardrail: Clear escalation rules for edge cases and full traceability. If a tool can’t show how it arrived at a suggestion, it shouldn’t touch a clinical decision. Establish explicit human review protocols for any AI-generated clinical content before it reaches patients or medical records.
Financial services
Banking.
- Service and back-office work: assistants summarize documents, draft responses, and reconcile data. JPMorgan reports approximately 30% fewer servicing calls per account in targeted Consumer and Community Banking segments and 15% lower processing costs in specific workflows.
- Risk and compliance: earlier risk flags, smarter anti-money-laundering reviews, and cleaner audit trails reduce losses and manual rework.
Insurance.
- Claims: straight-through processing for simple claims moves from days to hours.
- Underwriting: AI assembles files and surfaces risk signals so underwriters focus on complex judgment.
- Back office: finance, procurement, and HR automations deliver steady, compounding savings.
Leadership note: Treat service assistants and claims bots as products with roadmaps and release notes—not projects. That discipline keeps quality high as coverage expands.
Professional services (legal, consulting, accounting)
Document-heavy work is being rebuilt: contract and filing review, research synthesis, proposal generation. Well-scoped processes often see 40–60% time savings. . Major law firms report contract review cycles compressed from 8-12 hours to 2-3 hours for standard agreements, with associates redirected to judgment-heavy analysis and client advisory work.
Play to win: Build a governed retrieval layer over prior matters, proposals, and playbooks—your firm’s institutional memory—then give every practitioner an assistant that can reason over it.
Energy and utilities
Grid and renewables.
AI improves demand and renewable forecasting and helps balance the grid in real time. Autonomous inspections (drones plus computer vision) speed asset checks by 60-70% and reduce hazards. Predictive maintenance on critical infrastructure prevents outages—utilities report 20-30% reduction in unplanned downtime when AI is tied into work order systems and cuts truck rolls (field service visits).
How to scale: Start with one corridor or substation, prove inspection cycle time and fault detection, then expand with a standard data schema so models learn from every site.
Next Steps (practical and measurable)
1) Choose three processes—one for cost, one for revenue, one enabler.
Examples:
- Cost: customer service automation, predictive maintenance, the month-end finance close.
- Revenue: personalized offers, “next-best-action” in sales, improved online merchandising.
- Enabler: developer assistants for code and tests, HR screening and scheduling.
Write a one-line success metric and a quarterly target for each (e.g., “reduce average response time by 30%,” “increase conversion by 2 points,” “ship weekly instead of bi-weekly”).
2) Redesign the work, not just the process map.
Decide explicitly: what moves to the machine, what stays with people, where the hand-off happens, and what the quality gate is. Train for it. Incentivize it.
3) Industrialize fast.
Stand up a small platform team for identity, data access, monitoring, and policy. Establish lightweight model governance. Create a change backbone (playbooks, enablement, internal communications) so each new team ramps faster than the last.
4) Publish a value dashboard.
Measure cash, not demos: cost per contact, cycle time, on-shelf availability, release frequency, time-to-hire, revenue per visit. Baseline these metrics before launch—most teams skip this step and cannot prove impact six months later when challenged. Review monthly. Retire anything that doesn’t move the number.
5) Keep humans in the loop where it matters.
Customer experience, safety, financial risk, and regulatory exposure all require clear human decision points. Automate confidently—but design escalation paths from day one.
Final word
In 2025, AI pays where volume is high and rules are clear (service, supply chain, HR, engineering), and where personalization drives spend (marketing and sales). The winners aren’t “using AI.” They are re-staging how the work happens—and they can prove it on the P&L.