The Importance of Value Driver Trees and Benefit Realization Management in Digital Transformation
Digital transformation is not just about implementing new technologies—it is about generating real, measurable business value. Too often, organizations invest in digital initiatives without a clear understanding of how these efforts contribute to strategic goals, leading to wasted resources and unfulfilled expectations. I could have put this tool as well in the Strategy to Plan section, since you will need these insights already when setting up a transformation. Due to it’s focus on Sustainable Value Creation you find it here.
To ensure digital transformation delivers tangible benefits, organizations need structured approaches that tie initiatives to business value. Value Driver Trees (VDT) provide a visual and analytical way to break down how value is created, while Benefit Realization Management (BRM) ensures that transformation initiatives deliver the expected outcomes. By integrating these two approaches, organizations can bridge the gap between strategy and execution, ensuring every initiative contributes to meaningful business impact.
This article explores these frameworks, their interaction, and provides a step-by-step guide for implementing them effectively in digital transformation initiatives.
Understanding the Approaches
1. Value Driver Tree (VDT)
A Value Driver Tree (VDT) is a structured framework that breaks down an organization’s high-level business objectives into actionable and measurable components. It helps leaders identify the key levers that drive financial and operational performance.
Example: VDT for Retail e-Commerce Growth
Goal: Increase e-Commerce Revenue
👉 Sales Volume Growth
🔹 Improve Website Conversion Rate
🔹 Increase Traffic via Digital Marketing
👉 Average Order Value Increase
🔹 Personalized Product Recommendations
🔹 Bundled Pricing Strategy
👉 Customer Retention Improvement
🔹 Loyalty Program Enhancements
🔹 Improved Customer Support Response Time
This hierarchical breakdown helps organizations prioritize initiatives that have the most impact on revenue growth. Below one more example from the web on how to look at Value Drivers/KPIs.
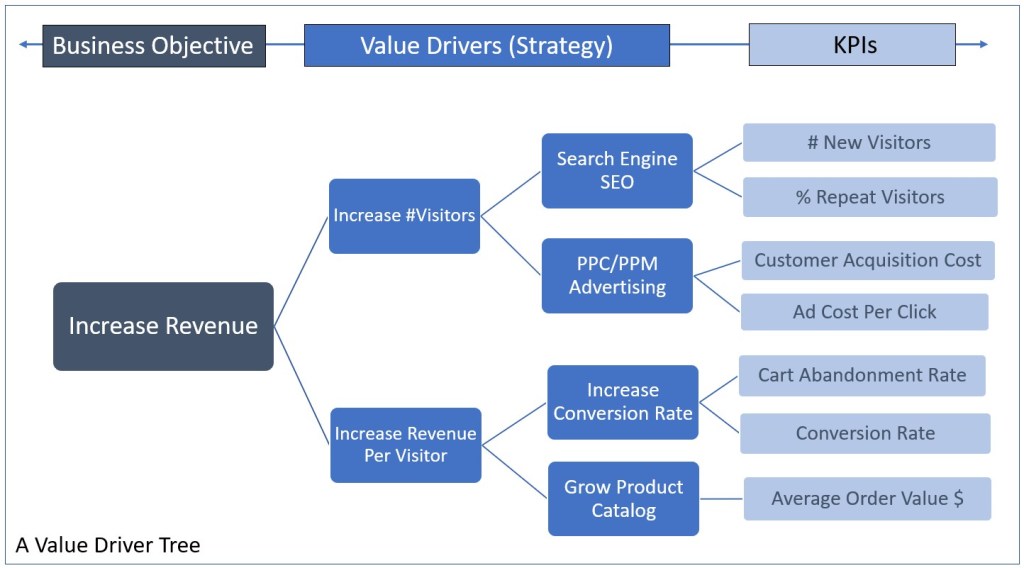
2. Benefit Realization Management (BRM) – PMI Approach
PMI’s Benefit Realization Management (BRM) framework provides a structured approach to ensure that projects and programs deliver measurable benefits that align with strategic objectives. It consists of three key phases:
- Benefit Identification: Define expected benefits, align them with strategic goals, and establish key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Benefit Execution: Monitor benefits realization through governance and stakeholder engagement during project execution.
- Benefit Sustainment: Ensure ongoing measurement and reinforcement of benefits post-project completion.
Example: BRM in an ERP Implementation
Objective: Improve Operational Efficiency Through an ERP System
👉 Benefit: Reduced Order Processing Time
🔹 Initiative: Automate manual order entry processes
🔹 KPI: Reduce order processing time from 48 hours to 12 hours
👉 Benefit: Lower IT Costs
🔹 Initiative: Consolidate legacy systems into a unified ERP platform
🔹 KPI: Reduce IT maintenance costs by 30%
By applying BRM, organizations can ensure that digital transformation projects remain focused on delivering real business benefits rather than just implementing technology for technology’s sake.
How VDT and BRM Interact
VDT and BRM complement each other by linking high-level business value drivers with structured benefit realization processes. Here’s how they work together:
- VDT Identifies Key Business Drivers → Helps organizations understand where value comes from.
- BRM Ensures Benefits Are Tracked and Realized → Ensures projects are aligned with value drivers and measured effectively.
- VDT Provides a Data-Driven Basis for Prioritization → Helps select the most impactful initiatives.
- BRM Embeds Value Tracking into Governance → Ensures sustained realization of benefits post-implementation.
By integrating VDT and BRM, organizations can establish a clear, data-driven transformation roadmap and ensure continuous value creation.
Implementation Plan
Step 1: Develop a Value Driver Tree
- Identify overarching business objectives (e.g., revenue growth, cost reduction, customer experience enhancement).
- Break them down into measurable value drivers and initiatives.
- Assign KPIs to each driver to establish clear tracking mechanisms.
Step 2: Align BRM to the Value Driver Tree
- Define benefits based on value drivers.
- Create a Benefits Dependency Network mapping initiatives to expected benefits.
- Assign accountability for benefit realization.
Step 3: Establish Governance and Measurement
- Integrate benefit tracking into program governance.
- Set up regular benefit reviews (e.g., quarterly assessments).
- Adjust strategies if expected benefits are not materializing.
Example: Applying VDT and BRM in a Digital Transformation Initiative
Scenario: A Bank’s Digital Banking Transformation
Step 1: Develop a Value Driver Tree
Goal: Enhance Digital Banking Experience
👉 Increase Mobile App Adoption
🔹 Simplify Onboarding Process
🔹 Improve User Interface & Experience
👉 Reduce Customer Support Costs
🔹 Introduce AI-powered Chatbots
🔹 Automate Fraud Detection Alerts
Step 2: Align BRM to VDT
| Benefit | KPI | Initiative | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Mobile Adoption | % of active users | UX Redesign | Monthly user growth rate |
| Lower Support Costs | Reduction in live calls | AI Chatbot Deployment | Call volume trend |
| Increased Security | Fraud incident reduction | AI-driven fraud detection | Fraud report metrics |
Step 3: Governance & Tracking
- Regular executive reviews track realized vs. projected benefits.
- Adjustments made based on data insights and customer feedback.
Conclusion: Driving Digital Transformation Success with VDT and BRM
Successful digital transformation requires more than just implementing technology—it demands a structured approach to ensure value realization. By leveraging Value Driver Trees (VDT) and Benefit Realization Management (BRM) together, organizations can:
✅ Clearly define how transformation initiatives contribute to business objectives.
✅ Prioritize efforts based on quantifiable value impact.
✅ Continuously track and adjust for sustained benefit realization.
To drive real business outcomes, organizations should integrate these frameworks into their transformation governance, ensuring a clear line of sight from strategic objectives to measurable benefits.
Call to Action
If your organization is embarking on a digital transformation journey, start by building your Value Driver Tree and structuring a Benefit Realization Framework. Need help applying these methods? Let’s discuss how to tailor them to your organization’s needs.









