Introduction
In today’s fast-moving business environment, companies must regularly reflect on how they generate value and translate this into effective business models. Organizations can operate multiple business models simultaneously, combining products and services, and within each model, there can be various versions of value chains (e.g., Software as a Service, Product as a Service, Information as a Service).
All these value chains must be executed efficiently within the company’s processes and systems. A great strategy without the right operational backbone is bound to fail. This article provides a structured approach to designing and optimizing value chains, supported by industry best practices.
1. Business Models: The Foundation of Value Creation
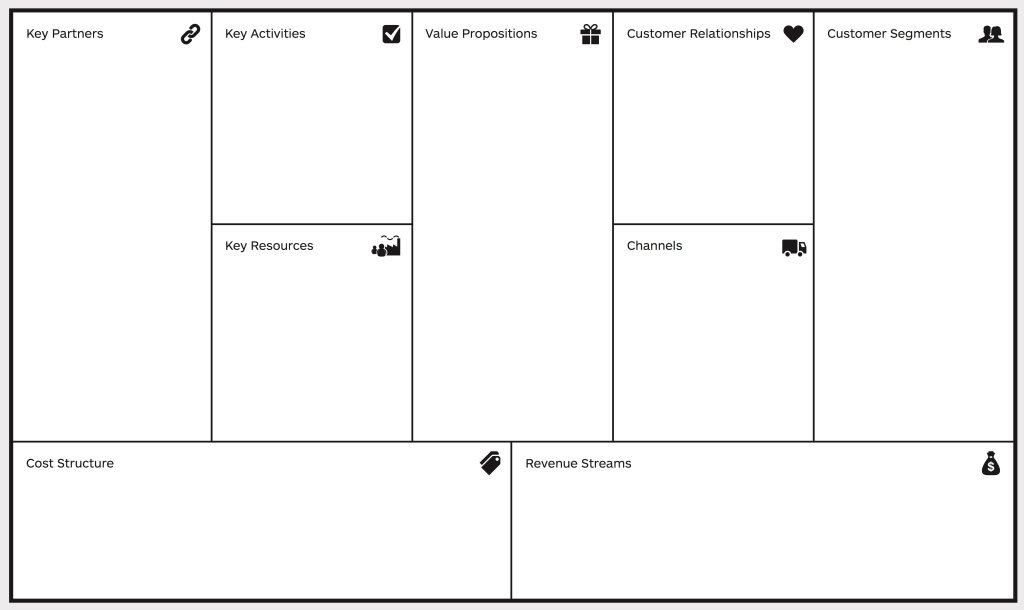
A business model describes how a company creates, delivers, and captures value. The Business Model Canvas (BMC), developed by Alexander Osterwalder, provides a structured framework to outline key business components.
The Business Model Canvas – Key Components
- Customer Segments – Who are we creating value for?
- Value Propositions – What unique value do we deliver?
- Channels – How do we reach customers?
- Customer Relationships – How do we interact with customers?
- Revenue Streams – How do we generate revenue?
- Key Resources – What assets do we need?
- Key Activities – What critical actions drive our value proposition?
- Key Partnerships – What external players support us?
- Cost Structure – What are the main costs of running our model?
The BMC offers a strategic blueprint, but executing it efficiently requires a well-structured value chain.
2. The Value Chain: Translating the Business Model into Execution
A value chain, as introduced by Michael Porter, breaks down a company’s activities into primary and support activities, helping companies understand how value is created, where efficiencies can be gained, and where competitive advantage can be built.
How the Value Chain Aligns with the Business Model Canvas
| Business Model Component | Corresponding Value Chain Activities |
|---|---|
| Key Activities | Defines core primary activities such as operations, logistics, and marketing. |
| Key Resources | Aligns with support activities like technology, HR, and procurement. |
| Key Partnerships | Influences supply chain design and outsourcing decisions. |
| Cost Structure | Determines cost-efficiency priorities within the value chain. |
| Revenue Streams | Shapes customer service, sales processes, and after-sales support. |
| Channels | Defines logistics, distribution, and digital engagement strategies. |
By aligning the business model with the value chain, companies ensure that strategy translates into action efficiently.
3. Using the Business Model Canvas to Optimize the Value Chain
To effectively link business model design and value chain execution, executives can follow these steps:
Step 1: Define the Business Model with the BMC
- Map out the nine components of your business model.
- Identify the most critical elements that drive differentiation and profitability.
Step 2: Mapping the Value Chain Based on the Business Model
Once a company has defined its business model, the next step is to ensure that its value chain is structured to deliver on that strategy.
Key Actions in Value Chain Mapping:
- Identify Primary Activities – Core operations that create and deliver value.
- Identify Support Activities – The enablers that ensure efficiency and sustainability.
- Assess Alignment – Ensuring every activity reinforces the business model.
Example: Amazon’s Primary Activities
- Inbound Logistics: Leverages an advanced supply chain with vast warehousing & supplier integration.
- Operations: Runs automated, AI-driven fulfillment centers to optimize costs and speed.
- Outbound Logistics: Owns Amazon Prime delivery & logistics rather than relying on third-party couriers.
- Marketing & Sales: Uses data-driven recommendations, digital advertising, and memberships for retention.
- Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots, 24/7 customer support, and seamless return processes.
📌 Takeaway: Amazon’s business model (e-commerce + logistics) succeeds because its value chain supports ultra-fast, cost-effective fulfillment.
Example: Apple’s Support Activities
- Firm Infrastructure: Centralized design & marketing strategy in California, manufacturing in China via Foxconn.
- HR Management: Attracts world-class talent, focusing on innovation and brand culture.
- Technology Development: Heavy investment in R&D, patents, and ecosystem lock-in (iOS, App Store).
- Procurement: Strong global supplier agreements for critical components like microchips & OLED screens.
📌 Takeaway: Apple’s business model (premium design & ecosystem lock-in) is supported by an R&D-driven value chain.
4. Aligning the Value Chain with Competitive Strategy
Once a company maps its value chain, the final step is ensuring it aligns with its competitive strategy. This means optimizing the value chain to reinforce cost leadership, differentiation, or innovation.
Three Strategic Approaches to Value Chain Optimization
1️⃣ Cost Leadership – Competing on price by minimizing costs and optimizing efficiency.
2️⃣ Differentiation – Competing on uniqueness by offering superior quality, service, or branding.
3️⃣ Innovation & Agility – Competing on speed, adaptability, and digital transformation.
1. How to Align the Value Chain with Cost Leadership:
✔ Inbound Logistics: Optimize supply chain efficiency by sourcing cost-effective materials and reducing waste (e.g., bulk purchasing, supplier consolidation).
✔ Operations: Automate manufacturing and streamline processes to reduce labor and production costs (e.g., lean manufacturing, Six Sigma, AI-powered automation).
✔ Outbound Logistics: Optimize distribution to lower transportation costs (e.g., route optimization, just-in-time delivery).
✔ Marketing & Sales: Leverage data-driven performance marketing to reduce customer acquisition costs (e.g., digital-only campaigns, AI ad targeting).
✔ Customer Service: Use self-service technology (e.g., chatbots, AI-driven support) to reduce support costs.
Example: Ryanair (Cost Leadership Strategy)
- Uses secondary airports with lower landing fees.
- Standardizes on a single aircraft type (Boeing 737) to reduce maintenance costs.
- No ticketing offices—100% online sales eliminate distribution costs.
- Charges for extras (baggage, seat selection) to keep ticket prices low.
📌 Takeaway: Ryanair’s low-cost airline model is viable because its value chain aggressively minimizes costs at every stage.
2. How to Align the Value Chain with Differentiation:
✔ Inbound Logistics: Secure high-quality, exclusive, or ethically sourced materials (e.g., luxury fashion, premium coffee beans, rare tech components).
✔ Operations: Invest in craftsmanship, advanced R&D, or personalization to create a unique product (e.g., Tesla’s self-driving AI, Apple’s design-first approach).
✔ Outbound Logistics: Create a premium experience (e.g., Apple’s seamless unboxing & in-store Genius Bar support).
✔ Marketing & Sales: Use brand storytelling, exclusivity, and high-touch engagement (e.g., Nike’s athlete-driven branding).
✔ Customer Service: Offer concierge-level, loyalty-driven experiences (e.g., luxury car brands providing VIP treatment).
Example: LVMH (Differentiation Strategy)
- Sources exclusive, rare materials for brands like Louis Vuitton, Dior, and Moët & Chandon.
- Maintains in-house artisanal production in Italy and France rather than outsourcing.
- Uses flagship stores in premium locations rather than mass-market retailers.
- Relies on celebrity endorsements, elite fashion events, and exclusivity-driven advertising.
📌 Takeaway: LVMH’s ability to command premium pricing comes from a value chain designed for brand exclusivity, quality, and aspirational appeal.
3. How to Align the Value Chain with Innovation & Agility:
✔ Inbound Logistics: Maintain flexible supply chains to adapt quickly to new trends and demands.
✔ Operations: Use digital technology, cloud-based infrastructure, and AI to enable rapid iteration.
✔ Outbound Logistics: Deploy agile distribution models to support real-time customer needs.
✔ Marketing & Sales: Leverage data, AI, and personalization for hyper-targeted engagement.
✔ Customer Service: Implement predictive and proactive AI-driven service to enhance experience.
🔹 Example: Spotify (Digital Streaming Disruption)
- Inbound Logistics: Uses a data-driven licensing model to determine which songs and artists to feature based on listening patterns.
- Operations: Invests in machine learning algorithms for personalized recommendations (e.g., “Discover Weekly”).
- Outbound Logistics: No physical distribution; everything is delivered via cloud-based streaming.
- Marketing & Sales: Uses AI-driven insights to personalize marketing, and leverages artist partnerships for exclusive content.
- Customer Service: Focuses on frictionless digital experience, self-service help centers, and AI-driven chat support.
📌 Takeaway: Spotify’s competitive edge in music streaming comes from an AI-powered, data-driven value chain that enables agility and innovation.
5. Key Takeaways
For businesses aiming to build competitive advantage, aligning the Business Model Canvas with a well-structured value chain is essential.
✅ A business model defines intent → The value chain ensures execution.
✅ Use the Business Model Canvas to clarify strategic priorities.
✅ Map your value chain to identify inefficiencies and enhance competitive advantage.
✅ Leverage digital tools to enhance agility in execution.
By continuously aligning strategy with execution, companies can drive sustainable growth and operational excellence.
Conclusion
In the era of digital transformation and competitive disruption, companies must ensure their value chain supports their business model effectively. The Business Model Canvas provides a clear framework to define strategy, while Value Chain Analysis ensures efficient execution.
Executives who successfully integrate these frameworks will position their organizations for long-term success, resilience, and market leadership.